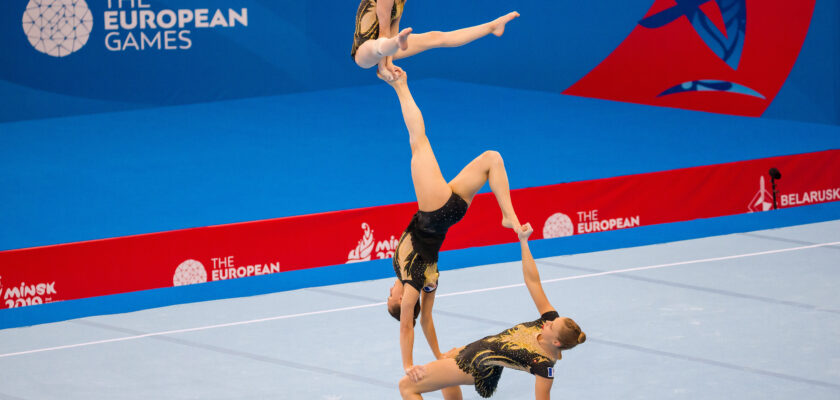
Muscle strength, agility, flexibility and precision. Gymnasts need to be extremely coordinated and have a good spatial understanding to perform the complex movements safely and effectively. Learn all about Acrobatic Gymnastics now!
Open your Betano account and get up to 1,000 reais in bonuses.
Payments via PIX, live games and super odds!
Click here to open your account!
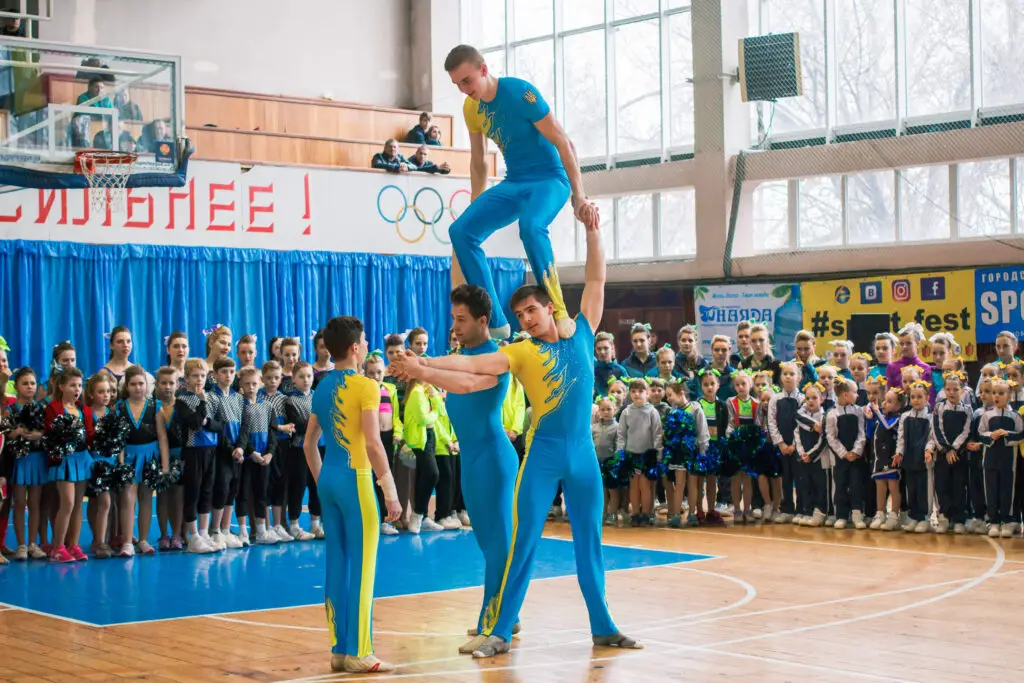
Read to the end and find out all about acrobatic gymnastics!
All about Acrobatic Gymnastics: history
Acrobatic gymnastics has manifested itself in different ways and in different cultures over the millennia;
The first traces of acrobatics were found in the art of the Bronze Age and were also referred to in Homer’s epic poems, as well as being present in the banquets of Ancient Greece and the harvest festivals of the Han Dynasty in China;
It also served as a form of entertainment for European courts during the Middle Ages.
Acrobatic gymnastics developed significantly from the 17th century, especially with the emergence of the circus;
However, as a sport, this discipline is relatively recent. The first international competitions took place in 1770;
Read to the end and find out all about acrobatic gymnastics!
Development as a modality
Acrobatic gymnastics began to consolidate itself as a discipline through the use of apparatus and acrobatics, which highlight human physical abilities;
The initial standards of competition were established in the Soviet Union, where large crowds gathered to watch athletic spectacles, such as the formation of huge human pyramids.The first Soviet national championships took place in 1939.
International expansion
The first international tournament known as “Sport Acrobatics” was held in Warsaw in 1957, with four teams taking part;
The International Federation of Sports Acrobatics (IFSA) was founded in 1973, and the first world championship was held the following year in Moscow, with teams from Bulgaria, West Germany, Great Britain, Hungary, Poland, the Soviet Union and the United States taking part.
In 1998, the IFSA was dissolved and the discipline was integrated into the International Gymnastics Federation, and has been known as Acrobatic Gymnastics since 2007.
Read to the end and find out all about acrobatic gymnastics!
Olympic start
Acrobatic gymnastics made its first appearance at the Summer Youth Olympic Games in Buenos Aires 2018;
The competition was played in the mixed doubles format and was won by Bulgarians Mariela Kostadinova and Panayot Dimitrov, who were also part of the team that won the gold medal in the team event, featuring gymnasts from different National Olympic Committees and from the four disciplines:
- Artistic
- Rhythmic
- Trampoline
- Acrobatics
Read to the end and find out all about acrobatic gymnastics!
All about Acrobatic Gymnastics: how does it work?
In the formation of pairs and groups in acrobatic gymnastics, we find athletes of different ages and sizes, categorized into three groups: basics, intermediates and flyers.
The bases, usually the most experienced and tallest members, are the strongest, which makes it easier for them to support the steering wheels;
Midfielders, on the other hand, are typically younger, with a smaller and lighter physical structure, which helps them execute team movements and prolongs their sporting career;
As well as promoting excellent athletic development, this discipline strengthens the bonds of friendship between participants, fostering a spirit of cooperation and, above all, mutual trust between athletes and coaches who work together in harmony.
Read to the end and find out all about acrobatic gymnastics!
Presentations
The performances take place in a 6×6 meter space, similar to those used in artistic gymnastics.
The groups of acrobats must perform up to three types of routines: one static, one dynamic and one combined.
Static routines are characterized by calmer movements, focused on strength and stability.
The dynamic routines are more energetic, incorporating elements of the gymnasts’ throws and aerial movements.
The combined routines, used in the final phases, combine static and strength exercises with varied skills, integrating aspects of general gymnastics.
Read to the end and find out all about acrobatic gymnastics!
Categories
- Female pair;
- Mixed pair;
- Male pair;
- Female trio;
- Men’s court.
All about Acrobatic Gymnastics: types of acrobatics
In acrobatic gymnastics, acrobatics are often classified by their characteristics and the way they are performed. Some of the common names and types of acrobatics include:
Jumping and throwing
- Hand Jump: the gymnast is launched from their partner’s hands.
- Planche throw: the gymnast is thrown while maintaining the planche position.
Equilibrisms
- Hand Balance: maintaining balance on one or two hands, often in inverted positions.
- Shoulder balance: the gymnast is supported on their partner’s shoulders.
Human Pyramids
- Three- or Four-Level Pyramids: structures made up of several gymnasts stacked on top of each other.
- Two-Person Pyramids: simpler structures with two gymnasts, often used as a base.
Read to the end and find out all about acrobatic gymnastics!
Rotation
- 360 Degree Spin: complete rotation in the air, often performed during launches.
- 180 Degree Rotation: partial rotation, common in transitions between movements.
Power Devices and Elements
- Planche: maintaining a horizontal position with the body supported by the arms.
- Death Lift: lifting the partner into the air, keeping the position fixed.
Ground and Synchronized Movements
- Jumps and Spins: movements that combine jumps and spins on the ground.
- Synchronized Movements: specific agreements where all team members perform equal or coordinated movements.
Read to the end and find out all about acrobatic gymnastics!
All about Acrobatic Gymnastics: rules and regulations
The rules of an acrobatic gymnastics competition are established to guarantee the safety, fairness and quality of the performances;
Competition format
Competitions can be held in pairs or small groups (trios or quartets).
The routines are divided into three types: Static, Dynamic and Combined.
Execution time
Each routine has a specific time limit. The duration may vary depending on the category and stage of the competition.
Routine structure
- Static Routine: focused on strength and balance movements, generally without continuous movement.
- Dynamic Routine: includes fast movements and acrobatic elements such as throws and jumps.
- Combined Routine: integrates static and dynamic elements, showing the versatility of the gymnasts.
Read to the end and find out all about acrobatic gymnastics!
Evaluation and scoring
The judges evaluate the routines based on specific criteria such as difficulty, execution, artistry and safety. Each criterion has a maximum and minimum score, and the final score is a sum of the points obtained in each criterion.
Criteria
- Difficulty: evaluates the complexity of the movements performed.
- Execution: focuses on precision, control and technical execution of movements.
- Artistic: considers the fluidity, presentation and choreography of the routine.
- Safety: checks the safety of movements, ensuring that gymnasts don’t take unnecessary risks.
Classification
Teams are ranked based on the total scores of their routines. In multi-stage competitions, teams can be eliminated or advance to the final stages based on their scores.
Read to the end and find out all about acrobatic gymnastics!
Changing gymnasts
Specific rules may apply to the substitution of gymnasts, especially in cases of injury or emergency.
Dress standards
Clothing must be appropriate for the competition, generally adherent and allowing freedom of movement without compromising safety.
Do you want to learn about other different sports? Now that you know all about acrobatic gymnastics, read on:



